
AI for Traditional Companies: A Strategic Guide to Smart Adoption
Discover how traditional companies can effectively adopt AI by focusing on real business challenges, ensuring readiness, and unlocking value without unnecessary costs.
AI for Traditional Companies: Smart Adoption Strategies
Traditional companies across industries face mounting pressure to integrate artificial intelligence into their operations. AI for traditional companies is not just about technology; it's about transforming business processes to achieve faster execution, reduced uncertainty, stronger decision-making, and improved operations. The key to successful AI adoption lies in starting from real operational pain points rather than chasing abstract technology trends.
AI adoption should start with business problems, not technology choices. Traditional companies that move carefully, validate early, and build on real needs can unlock measurable value without wasting time or budget on misaligned solutions.
Understanding AI Readiness for Traditional Businesses
Before diving into AI implementation, traditional companies must honestly assess their current state. AI readiness encompasses data quality, technical infrastructure, and organizational culture—not just the willingness to adopt new technology. Many brick-and-mortar businesses discover that their biggest obstacles aren't technical but rooted in people, processes, and organizational politics.
According to recent research, 45% of C-suite executives found the ROI of AI below expectations, with only 10% exceeding them. This gap often stems from unrealistic expectations and inadequate preparation rather than AI's inherent limitations.
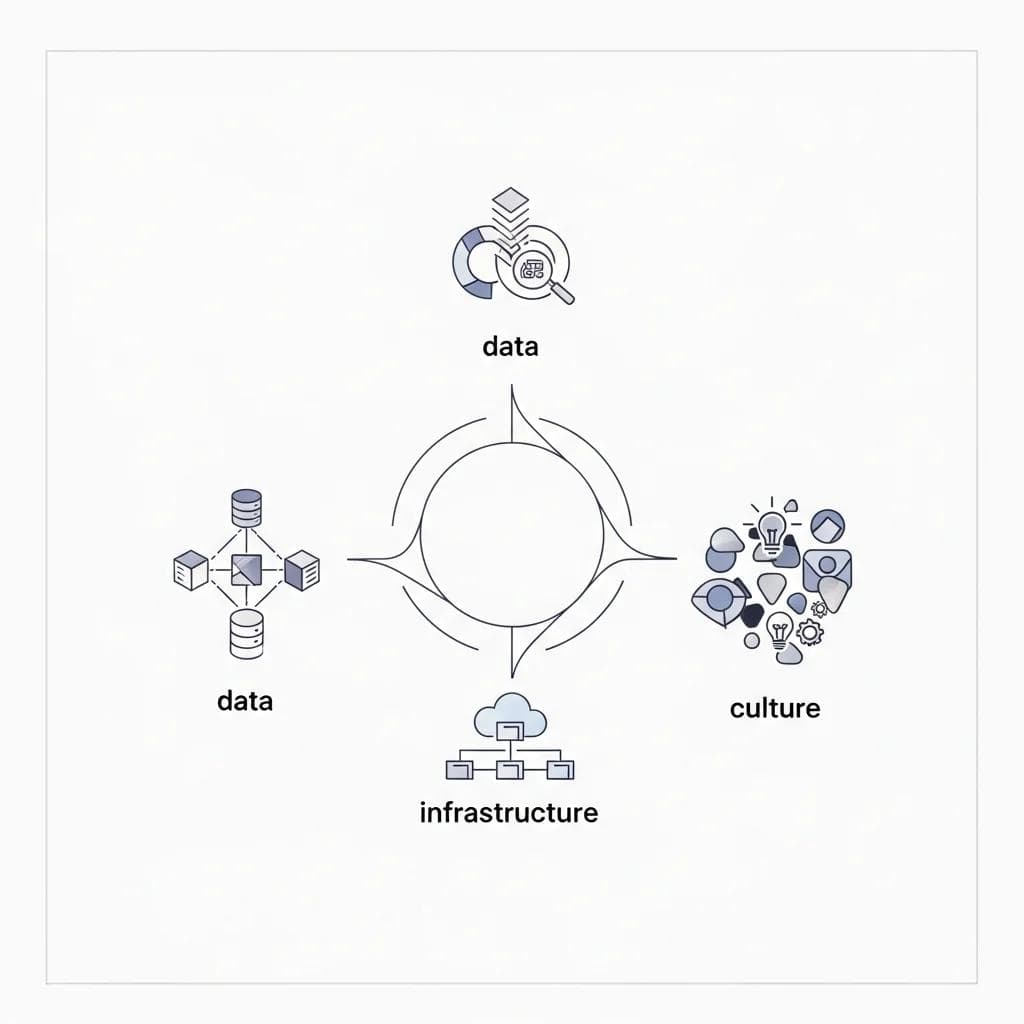
Infographic showing AI readiness assessment framework with data, infrastructure, and culture components.
Data Foundation Assessment
Your data is the fuel for any AI system. Poor data quality leads to inaccurate AI outputs, making data management practices the foundation of successful AI adoption. Traditional companies should evaluate:
- Data availability: What information do you currently collect and store?
- Data quality: Is your data clean, consistent, and accurate?
- Data accessibility: Can your systems easily share information across departments?
- Data governance: Do you have policies for data usage, privacy, and security?
Many traditional businesses collect valuable operational data but store it in disconnected systems or inconsistent formats. A manufacturing company might track production metrics in one system, quality data in another, and maintenance records in spreadsheets—creating barriers to AI implementation.
Infrastructure Evaluation
Legacy systems present both challenges and opportunities for AI integration. Rather than replacing entire systems, successful AI adoption often involves adding intelligence to existing processes through careful integration planning. Consider:
- Current technology stack compatibility
- Integration capabilities with existing software
- Scalability requirements for AI workloads
- Security protocols for AI-enhanced systems
The goal isn't to modernize everything at once but to identify where AI can enhance current operations without disrupting core business functions.
Identifying High-Impact AI Opportunities
The most successful AI implementations solve specific, measurable business problems rather than pursuing technology for its own sake. Traditional companies should focus on three primary areas where AI delivers immediate value: automating repetitive work, improving decision-making, and strengthening existing systems with intelligence.
Process Automation Opportunities
Start by mapping repetitive, rule-based tasks that consume significant employee time. These processes often represent the lowest-risk, highest-reward AI applications:
Customer Service Enhancement: Retail companies like Sephora have successfully implemented AI-powered virtual assistants that handle routine customer inquiries, freeing human agents to focus on complex issues. Their virtual beauty assistant provides personalized product recommendations, improving customer satisfaction while reducing support costs.
Document Processing: Traditional businesses often handle large volumes of invoices, contracts, or forms manually. AI can extract information, validate data, and route documents automatically, reducing processing time from hours to minutes.
Inventory Management: Predictive algorithms can analyze historical sales data, seasonal patterns, and external factors to optimize stock levels, reducing both overstock and stockout situations.
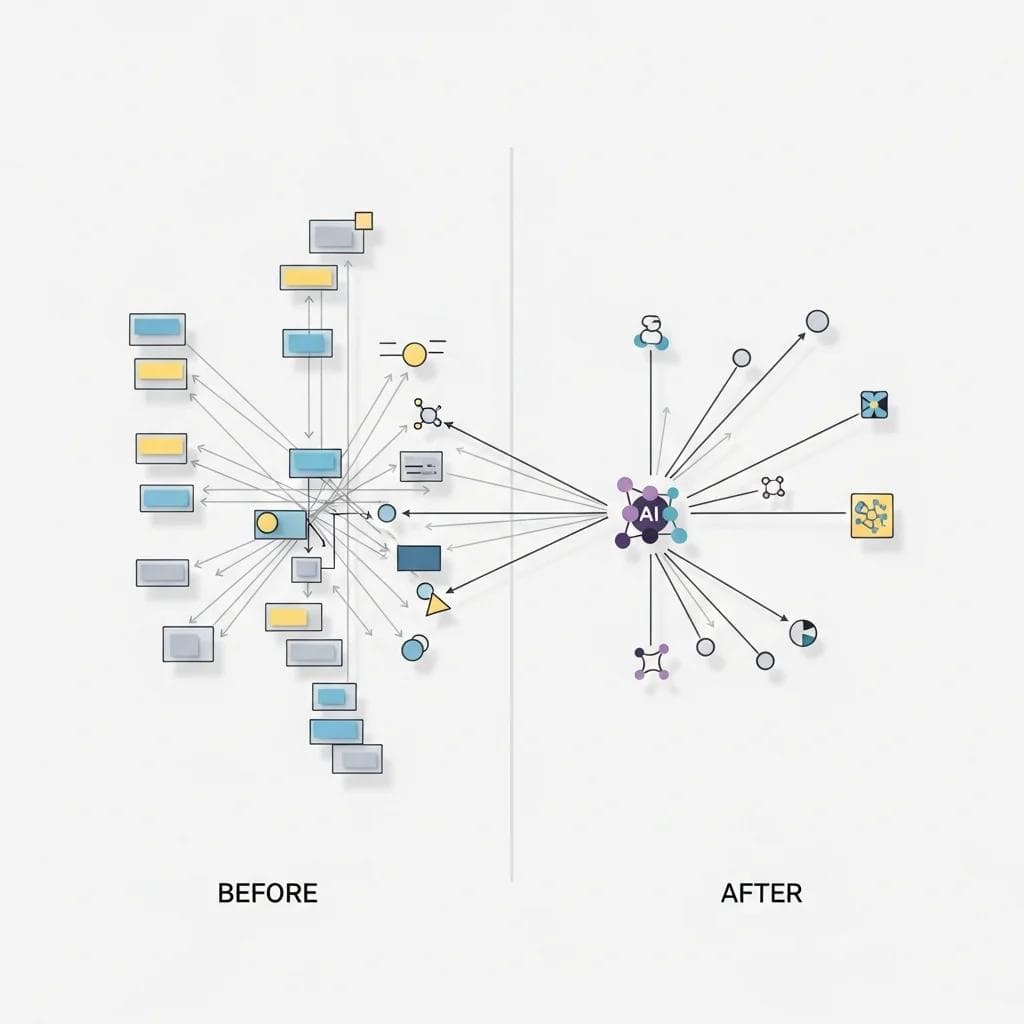
Process automation workflow diagram showing before and after AI implementation.
Decision-Making Enhancement
AI excels at analyzing large datasets to surface insights that inform better business decisions. Traditional companies can leverage AI to:
Demand Forecasting: Retail chains use AI to predict customer demand across locations, optimizing inventory distribution and reducing waste. Walmart employs machine learning algorithms to analyze purchasing patterns, weather data, and local events to improve forecasting accuracy.
Predictive Maintenance: Manufacturing companies implement AI-powered monitoring systems that analyze equipment sensor data to predict failures before they occur. Predictive maintenance using AI can reduce unexpected downtime by 30-50% while extending equipment lifespan through timely interventions.
Customer Segmentation: AI can analyze customer behavior patterns to identify distinct segments, enabling more targeted marketing campaigns and personalized experiences.
System Intelligence Integration
Rather than replacing existing systems, smart AI integration adds intelligence layers that enhance current capabilities:
Quality Control Enhancement: Manufacturing companies integrate computer vision systems with existing production lines to detect defects in real-time, improving quality while maintaining production speed.
Supply Chain Optimization: AI algorithms analyze supplier performance, transportation costs, and delivery times to recommend optimal sourcing and logistics decisions.
Financial Analysis: AI tools can analyze financial data patterns to identify cost-saving opportunities, detect anomalies, and improve budgeting accuracy.
Common AI Adoption Traps and How to Avoid Them
Understanding what not to do is often as valuable as knowing the right approach. Traditional companies frequently fall into predictable traps that waste resources and damage confidence in AI initiatives.
The "Shiny Object" Syndrome
Many organizations chase the latest AI tools without considering fit for their specific needs. Successful AI adoption requires matching technology capabilities to actual business requirements, not implementing popular solutions hoping they'll create value.
Trap: Adopting generative AI for content creation when your primary need is process automation.
Solution: Start with a clear problem definition before evaluating technology options.
Data Readiness Underestimation
78% of companies now use AI in at least one function, but many underestimate the data preparation required for success. Poor data quality remains the primary barrier to effective AI implementation.
Trap: Assuming existing data is "good enough" for AI without proper assessment.
Solution: Invest in data cleaning and standardization before implementing AI solutions.
Unrealistic Timeline Expectations
AI implementation requires time for data preparation, model training, testing, and integration—rushing the process typically leads to suboptimal results. Organizations often expect immediate transformation without allowing adequate development time.
Trap: Expecting AI to solve complex problems within weeks of implementation.
Solution: Plan for 3-6 month pilot projects with clear success metrics and iterative improvements.
Skills Gap Ignorance
Research shows that 61% of employees receive less than five hours of AI-related training. Without proper training and change management, even well-designed AI systems fail due to user resistance or misunderstanding.
Trap: Implementing AI tools without training employees on proper usage and integration.
Solution: Develop comprehensive training programs and change management strategies alongside technical implementation.
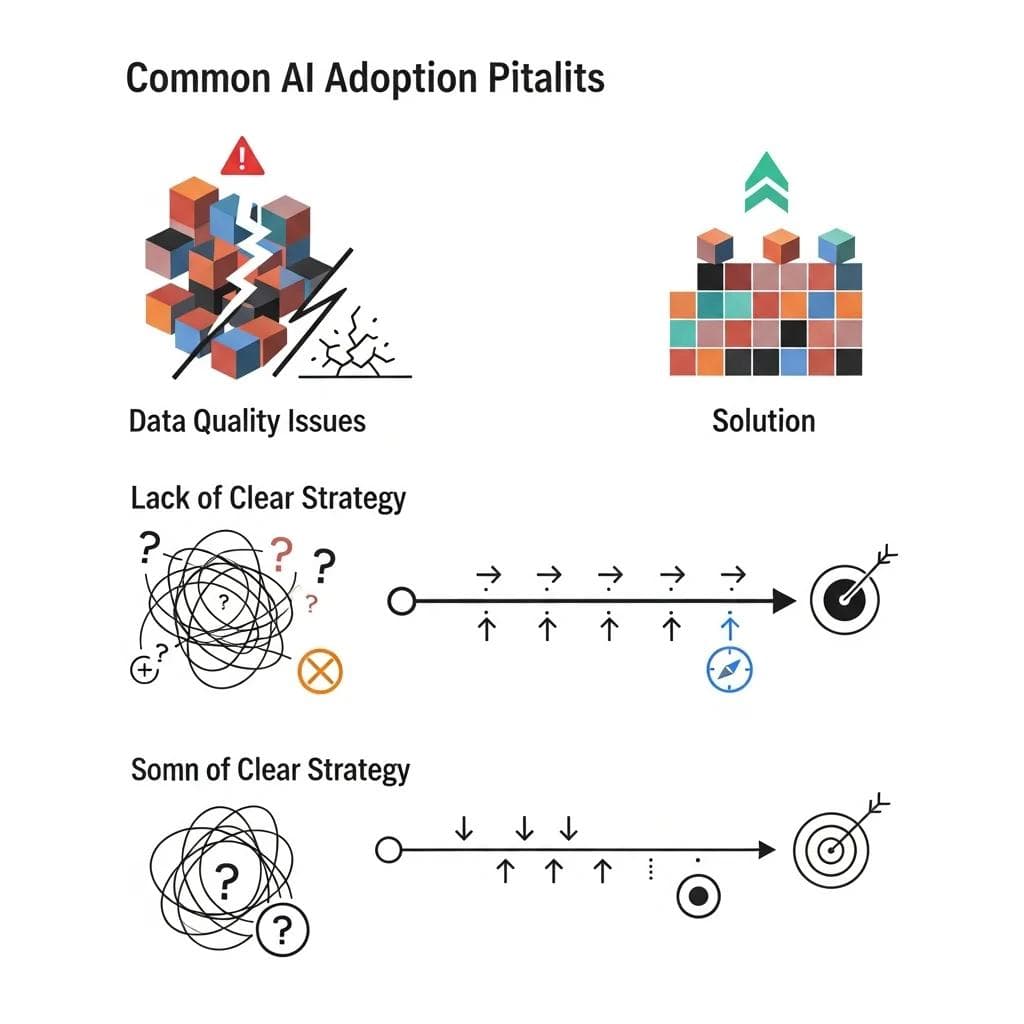
Common AI adoption pitfalls infographic with warning signs and solutions.
Building Your AI Implementation Roadmap
A structured approach to AI adoption reduces risk while maximizing the likelihood of success. Traditional companies should follow a phased implementation strategy that builds capability progressively.
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Months 1-3)
Data Audit and Preparation: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of current data assets, identifying quality issues and integration requirements. Clean and standardize priority datasets that support your initial AI use case.
Skills Assessment: Evaluate current team capabilities and identify training needs. Consider whether to build internal expertise or partner with external specialists for initial implementations.
Pilot Project Selection: Choose a specific, measurable problem with clear success criteria. Ideal pilot projects have:
- Well-defined scope and objectives
- Available, quality data
- Measurable business impact
- Limited organizational complexity
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation (Months 3-6)
Solution Development: Build or implement your chosen AI solution, focusing on integration with existing systems and workflows. Maintain close collaboration between technical teams and end users throughout development.
Testing and Validation: Rigorously test the solution with real data and user scenarios. Measure performance against baseline metrics and gather user feedback for improvements.
Change Management: Prepare employees for the new system through training, communication, and involvement in the testing process. Address concerns and resistance proactively.
Phase 3: Scaling and Optimization (Months 6-12)
Performance Analysis: Evaluate pilot results against success criteria, documenting lessons learned and improvement opportunities. Successful AI pilots typically show 20-30% improvement in targeted metrics within six months.
Expansion Planning: Identify additional use cases that can leverage similar AI capabilities or benefit from lessons learned in the pilot phase.
Governance Framework: Establish policies and procedures for AI use, including data governance, ethical guidelines, and quality assurance processes.
Real-World Success Stories
Learning from other traditional companies' AI journeys provides valuable insights and realistic expectations for your own implementation.
Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance Success
A mid-sized manufacturing company implemented AI-powered predictive maintenance after experiencing frequent equipment failures that disrupted production schedules. By analyzing sensor data from critical machinery, their AI system now predicts maintenance needs 2-3 weeks in advance.
Results: 40% reduction in unplanned downtime, 25% decrease in maintenance costs, and improved production consistency. The system paid for itself within 18 months through reduced emergency repairs and increased productivity.
Key Success Factors:
- Started with their most critical equipment
- Invested in proper sensor installation and data collection
- Trained maintenance staff to interpret AI recommendations
- Integrated predictions with existing maintenance scheduling systems
Retail: Customer Experience Enhancement
A regional retail chain implemented AI-powered customer service tools to handle routine inquiries and provide personalized product recommendations. Similar to Sephora's approach, they developed a virtual assistant that helps customers find products and answers common questions.
Results: 60% reduction in routine customer service calls, 15% increase in average transaction value through better recommendations, and improved customer satisfaction scores.
Key Success Factors:
- Focused on specific, repetitive customer inquiries
- Trained the AI system with actual customer interaction data
- Maintained human oversight for complex issues
- Continuously refined the system based on customer feedback
Financial Services: Fraud Detection
A community bank implemented AI-powered fraud detection to identify suspicious transactions in real-time. The system analyzes transaction patterns, customer behavior, and external risk factors to flag potential fraud.
Results: 50% improvement in fraud detection accuracy, 70% reduction in false positives, and faster customer service through reduced legitimate transaction blocks.
Key Success Factors:
- Started with clear fraud patterns and historical data
- Balanced security with customer experience
- Integrated with existing transaction processing systems
- Provided training for customer service staff on AI-flagged transactions
Success story timeline showing implementation phases and results.
Overcoming Organizational Resistance
Employee uncertainty about AI's role and fear of job replacement represent the primary organizational barriers to successful AI adoption. Traditional companies must address these concerns proactively through communication, training, and inclusive implementation approaches.
Building AI Literacy
Organizations should implement comprehensive AI education programs that demystify the technology and clarify its role in supporting rather than replacing human workers. Effective programs include:
- Basic AI concepts: Help employees understand what AI can and cannot do
- Practical applications: Show real examples relevant to their work
- Hands-on experience: Provide opportunities to interact with AI tools
- Ongoing support: Offer continued learning resources and assistance
Addressing Job Security Concerns
Research indicates that AI typically augments human capabilities rather than replacing workers entirely, but this message requires consistent communication and demonstration. Successful companies:
- Clearly communicate AI's role in supporting existing jobs
- Provide retraining opportunities for affected roles
- Involve employees in AI implementation planning
- Share success stories that highlight human-AI collaboration
Creating AI Champions
Identify enthusiastic early adopters who can serve as internal advocates and trainers. AI champions help bridge the gap between technical capabilities and practical applications, making adoption smoother across the organization.
Measuring AI Success and ROI
Clear metrics and measurement frameworks ensure AI investments deliver expected business value while identifying areas for improvement. Traditional companies should establish both quantitative and qualitative success indicators.
Quantitative Metrics
Cost Reduction: Measure direct savings from process automation, reduced errors, or improved efficiency. Track metrics like processing time, labor costs, and error rates before and after AI implementation.
Revenue Impact: Monitor increases in sales, customer retention, or market share attributable to AI-enhanced capabilities. This might include improved customer experiences, better product recommendations, or optimized pricing strategies.
Operational Efficiency: Track improvements in productivity, resource utilization, or quality metrics. Examples include faster decision-making, reduced waste, or improved asset utilization.
Qualitative Indicators
Employee Satisfaction: Survey staff about their experience with AI tools, including ease of use, impact on job satisfaction, and perceived value.
Customer Experience: Monitor customer feedback, satisfaction scores, and engagement metrics to assess AI's impact on service quality.
Decision Quality: Evaluate whether AI-supported decisions lead to better outcomes, even if the impact isn't immediately quantifiable.
ROI Calculation Framework
AI ROI should account for both direct financial returns and strategic benefits that may not immediately translate to revenue. Consider:
- Implementation costs (technology, training, integration)
- Ongoing operational expenses
- Direct financial benefits (cost savings, revenue increases)
- Strategic advantages (competitive positioning, capability building)
- Risk mitigation value (improved compliance, reduced errors)
ROI measurement dashboard showing key AI performance indicators.
Building Strategic AI Partnerships
Traditional companies often benefit from partnering with AI specialists rather than building all capabilities internally. Strategic partnerships can accelerate implementation while reducing risk and resource requirements.
When to Partner vs. Build Internal Capabilities
Partner for: Specialized technical expertise, initial implementations, complex integrations, and cutting-edge AI capabilities.
Build internally for: Core business logic, ongoing maintenance, user training, and strategic AI governance.
Selecting the Right AI Partners
Evaluate potential partners based on:
- Industry experience: Understanding of your sector's specific challenges and requirements
- Technical capabilities: Proven expertise in relevant AI technologies and integration approaches
- Implementation methodology: Structured approach to project management and risk mitigation
- Long-term support: Ongoing maintenance, updates, and strategic guidance capabilities
Partnership Success Factors
Successful AI partnerships require clear communication, defined responsibilities, and aligned objectives. Establish:
- Detailed project scope and deliverables
- Success metrics and accountability measures
- Knowledge transfer plans for internal team development
- Ongoing support and maintenance agreements
Frequently Asked Questions
How to start with AI in traditional businesses?
Begin by identifying specific operational pain points where AI can provide measurable improvements. Conduct a data audit to ensure data quality and accessibility, and select a pilot project with clear success criteria. Partner with AI specialists if needed to accelerate implementation.
What are AI challenges for brick-and-mortar companies?
Challenges include data quality issues, legacy system integration, employee resistance, and unrealistic expectations. Address these by investing in data management, planning integration carefully, providing training, and setting realistic timelines.
How long does it typically take to see results from AI implementation?
Most traditional companies see initial results within 3-6 months for focused pilot projects. However, significant transformation typically requires 12-18 months of sustained effort, including data preparation, system integration, and organizational adaptation.
What's the minimum budget required for meaningful AI adoption?
Successful AI pilots can start with budgets as low as $50,000-$100,000 for focused applications like process automation or basic analytics. However, enterprise-wide implementations typically require $500,000-$2 million investments over 12-24 months.
How do we handle employee concerns about job displacement?
Focus on AI as augmentation rather than replacement. Provide clear communication about AI's role, offer retraining opportunities, and involve employees in implementation planning. Most successful AI deployments enhance human capabilities rather than eliminate positions.
What if our data isn't perfect—should we wait to implement AI?
Perfect data isn't required, but adequate data quality is essential. Start with data cleaning and standardization as part of your AI initiative rather than waiting for perfect conditions. Many companies successfully implement AI while continuously improving their data quality.
Can small and medium businesses afford AI implementation?
Yes, cloud-based AI services and SaaS solutions make AI accessible to smaller organizations. Start with specific, high-impact use cases and leverage existing platforms rather than building custom solutions from scratch.
How do we choose between different AI technologies and vendors?
Start with your business problem, not the technology. Clearly define your requirements, evaluate solutions based on fit rather than features, and consider factors like integration complexity, ongoing support, and total cost of ownership.
What are the biggest risks in AI adoption for traditional companies?
The primary risks include poor data quality leading to inaccurate results, inadequate employee training causing resistance or misuse, unrealistic expectations creating disappointment, and insufficient integration planning disrupting existing operations.
How do we ensure our AI implementation remains compliant with regulations?
Work with legal and compliance teams from the beginning, choose AI solutions with built-in compliance features, maintain human oversight of AI decisions, and document your AI governance processes for regulatory review.
Should we start with generative AI or traditional machine learning?
Choose based on your specific use case. Traditional machine learning often provides better ROI for operational improvements like predictive maintenance or demand forecasting, while generative AI excels at content creation and customer interaction enhancement.
How do we measure success and prove ROI to stakeholders?
Establish clear baseline metrics before implementation, track both quantitative results (cost savings, efficiency gains) and qualitative improvements (customer satisfaction, employee experience), and calculate ROI including both direct financial returns and strategic benefits.
Conclusion: Your Path Forward
AI adoption success for traditional companies depends on starting with real business problems, moving carefully through structured implementation phases, and building organizational capabilities alongside technical solutions. The companies that thrive will be those that view AI as a tool for enhancing their existing strengths rather than a complete business transformation.
Begin your AI journey today by identifying key areas for improvement and partnering with experts. Focus on data quality, employee training, and gradual capability building rather than pursuing dramatic changes. The most successful AI implementations solve today's problems while building tomorrow's competitive advantages.
Remember that AI adoption is a marathon, not a sprint. Traditional companies that take a thoughtful, problem-first approach to AI implementation position themselves for sustainable success while avoiding the common pitfalls that derail less strategic initiatives. Your industry knowledge and operational expertise, combined with carefully chosen AI capabilities, create a powerful foundation for long-term competitive advantage.
The question isn't whether traditional companies should adopt AI—it's how quickly they can do so strategically and effectively. Start with one focused pilot project, learn from the experience, and build your AI capabilities systematically. The time to begin is now.
More Blog Posts

AI Agents: The Next Generation of Business Software Transforming Operations
Discover how AI agents are revolutionizing business operations by transforming software into proactive collaborators that anticipate needs and streamline complex processes autonomously.

AI Agents in Enterprise Workflows: Transforming Business Operations for 2026
Discover how AI agents are revolutionizing enterprise workflows, transforming businesses into proactive, autonomous entities that enhance efficiency and drive measurable value.

Scaling AI Solutions: From Prototype to Production Best Practices
Learn how to successfully scale AI solutions from prototype to production, focusing on key practices that align data engineering with business goals, especially in healthcare.