
AI in Manufacturing: From Buzzwords to Measurable Business Value
Discover how AI can enhance manufacturing operations through practical automation and decision support, delivering real value without disruptive overhauls.
AI in Manufacturing: Turning Buzzwords into Business Value
Manufacturing operations leaders face a constant barrage of AI promises, but most discussions remain frustratingly abstract. AI in manufacturing is transforming operations by integrating seamlessly with existing production lines. While vendors tout revolutionary transformation, practical questions persist: How does AI actually integrate with existing production lines? What specific operational improvements can you expect? Which applications deliver measurable returns?
AI creates value when it improves real workflows. The strongest results come from practical automation and decision support—not speculative transformation programs. This reality-based approach to AI implementation focuses on concrete operational improvements rather than disruptive overhauls.
Modern AI systems excel at enhancing existing processes through targeted automation, predictive analytics, and intelligent decision support. Instead of replacing entire workflows, today's most successful AI implementations augment human capabilities and optimize established operations. Organizations achieving the best results start with specific use cases—predictive maintenance, quality control, or scheduling optimization—then expand systematically based on proven outcomes.
What AI Actually Does in Manufacturing Operations
Artificial Intelligence in manufacturing refers to computer systems that can analyze data, recognize patterns, and make decisions to optimize production processes without constant human intervention. Unlike traditional automation that follows rigid programming, AI systems adapt to changing conditions and improve performance over time through machine learning.
The practical applications of AI in manufacturing center on five core capabilities: pattern recognition, predictive analytics, process optimization, quality assessment, and intelligent scheduling. These capabilities translate into tangible operational improvements when applied to specific manufacturing challenges.
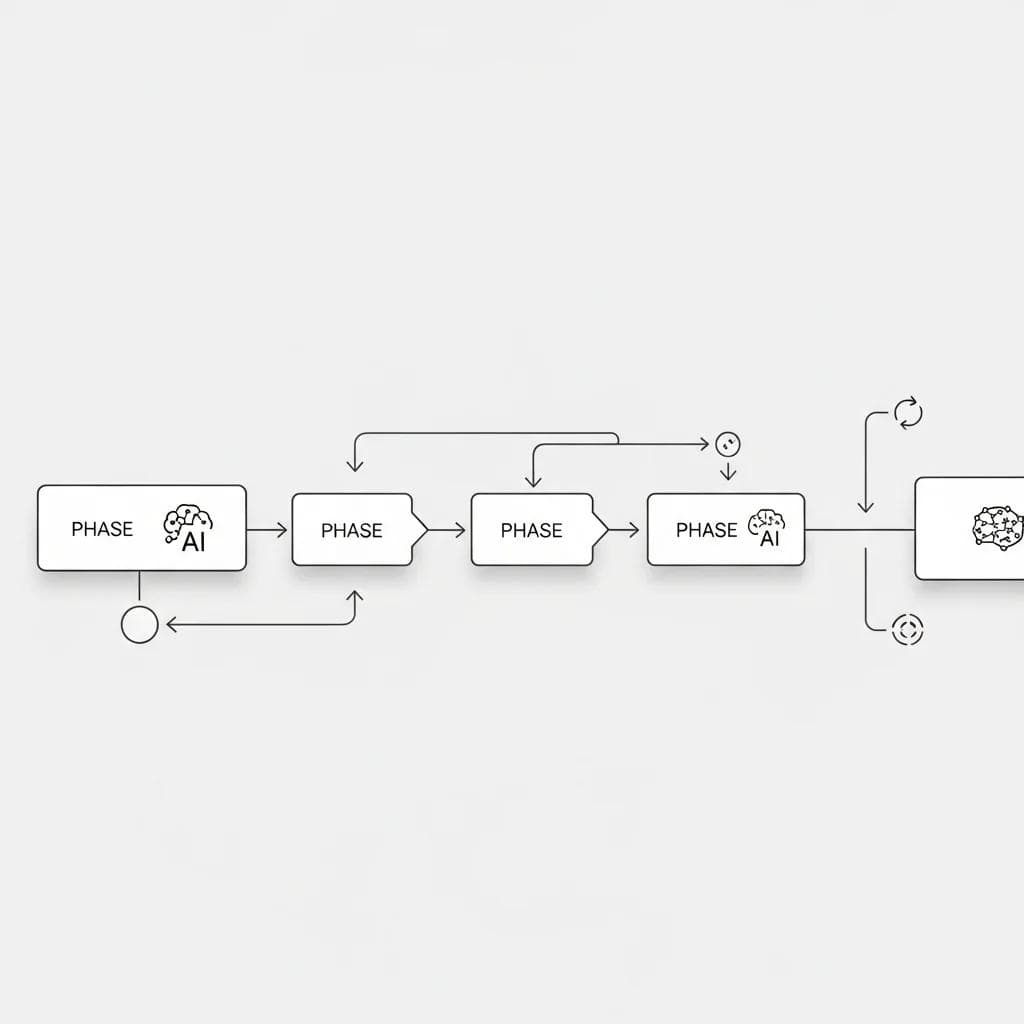
Flowchart showing phased AI implementation approach with feedback loops.
Pattern Recognition for Quality Control
AI-powered computer vision systems can identify defects, inconsistencies, and quality issues faster and more accurately than human inspectors. These systems analyze thousands of images per minute, detecting microscopic flaws that might escape visual inspection. According to MANTEC research, AI-powered computer vision for quality control achieves defect detection improvements of 90%.
A practical example involves automotive parts manufacturing, where AI vision systems inspect painted surfaces for scratches, dents, or color variations. The system learns from thousands of examples to distinguish acceptable variations from true defects, reducing false positives while catching genuine quality issues.
Predictive Analytics for Equipment Maintenance
Predictive maintenance represents one of AI's most mature manufacturing applications. By analyzing sensor data from equipment—vibration patterns, temperature fluctuations, power consumption, and operational cycles—AI systems can predict when machines are likely to fail or require maintenance.
IBM research shows that predictive maintenance reduces downtime by over 50% while extending equipment lifespan and optimizing maintenance schedules. This approach shifts maintenance from reactive repairs to proactive interventions, preventing costly breakdowns and unplanned production stops.
Process Optimization Through Data Analysis
AI systems continuously analyze production data to identify optimization opportunities. These systems examine variables like machine settings, material flow, environmental conditions, and production schedules to recommend adjustments that improve efficiency, reduce waste, or increase throughput.
The key advantage lies in AI's ability to process complex relationships between multiple variables simultaneously. While human operators might focus on one or two factors, AI can optimize across dozens of parameters in real-time.
Practical Applications That Deliver Results
Forecasting and Demand Planning
Manufacturing organizations struggle with demand forecasting accuracy, leading to overproduction, stockouts, or inefficient resource allocation. AI-powered forecasting systems analyze historical sales data, market trends, seasonal patterns, and external factors to generate more accurate demand predictions.
These systems typically improve forecasting accuracy by 20-30% compared to traditional statistical methods, directly impacting inventory costs and production planning efficiency. The improvement comes from AI's ability to identify subtle patterns in complex datasets and adapt to changing market conditions.
A food processing company implemented AI forecasting to predict seasonal demand for frozen products. The system analyzed weather patterns, holiday schedules, promotional activities, and historical sales data to generate weekly production forecasts. The result was a 25% reduction in inventory holding costs and 15% fewer stockouts during peak seasons.

AI-powered quality control system inspecting electronic components on assembly line.
Intelligent Quality Control Systems
Traditional quality control relies on sampling inspections that may miss defects or create bottlenecks in production flow. AI-powered quality systems perform continuous, comprehensive inspections without slowing production.
These systems use multiple technologies:
- Computer vision for visual defect detection
- Acoustic analysis for identifying mechanical issues
- Sensor fusion for comprehensive quality assessment
- Statistical process control enhanced with machine learning
An electronics manufacturer deployed AI quality control on their circuit board assembly line. The system inspects 100% of boards using high-resolution cameras and specialized lighting, identifying solder defects, component placement errors, and trace damage. Implementation resulted in a 40% reduction in customer returns and 60% faster quality inspections.
Production Scheduling Optimization
Manufacturing scheduling involves complex decisions about resource allocation, job sequencing, and capacity utilization. AI scheduling systems consider multiple constraints simultaneously: machine availability, operator skills, material supply, delivery deadlines, and setup times.
AI-driven scheduling typically improves overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by 15-25% while reducing setup times and minimizing production bottlenecks. The systems continuously adjust schedules based on real-time conditions, equipment status, and changing priorities.
Customer Support Enhancement
AI transforms manufacturing customer support through intelligent case routing, automated troubleshooting, and predictive service recommendations. These systems analyze customer inquiries, equipment data, and service history to provide faster, more accurate support.
Chatbots handle routine inquiries about product specifications, delivery status, or basic troubleshooting. More sophisticated AI systems analyze equipment telemetry data to predict service needs and proactively contact customers before issues become critical.
An industrial equipment manufacturer implemented AI-powered customer support that analyzes machine data from connected devices. The system identifies performance anomalies and automatically creates service tickets with recommended actions. This proactive approach reduced emergency service calls by 35% and improved customer satisfaction scores.
Internal Reporting and Analytics
AI-powered reporting systems transform raw operational data into actionable insights. Instead of static reports, these systems provide dynamic dashboards that highlight trends, anomalies, and optimization opportunities.
Key capabilities include:
- Automated anomaly detection in production metrics
- Trend analysis for long-term planning
- Root cause analysis for quality or efficiency issues
- Predictive insights for operational planning
Integration with Existing Workflows
Modern AI systems integrate with existing workflows instead of replacing them, creating hybrid human-AI operations that leverage the strengths of both. This integration approach reduces implementation risk while maximizing the value of existing investments in equipment, systems, and employee expertise.
Augmenting Human Decision-Making
Rather than replacing human judgment, AI systems provide data-driven insights that enhance decision-making. Operators receive recommendations, alerts, and analysis that inform their choices while maintaining control over critical decisions.
A chemical processing plant implemented AI-powered process optimization that continuously analyzes reactor conditions and suggests parameter adjustments. Operators review these recommendations and decide whether to implement changes based on their understanding of current conditions and production goals. This collaboration improved yield by 12% while maintaining operator expertise and control.
Working with Legacy Systems
Most manufacturing facilities operate with a mix of modern and legacy equipment. Successful AI implementations work within these constraints by:
- Connecting to existing sensors and control systems
- Using edge computing to process data locally
- Integrating with current MES/ERP systems
- Providing APIs for custom integrations
Phased Implementation Approach
The most successful AI implementations follow a phased approach, starting with pilot projects that demonstrate value before expanding to broader applications. This strategy minimizes risk while building organizational confidence and expertise.
Phase 1: Pilot Project - Select a specific use case with clear success metrics
Phase 2: Validation - Measure results and refine the system
Phase 3: Expansion - Apply learnings to similar applications
Phase 4: Integration - Connect multiple AI systems for broader optimization
Small Automations, Big Results
Small, targeted automations can produce outsized gains when applied to high-frequency, high-impact processes. This principle guides successful AI implementations that focus on specific operational pain points rather than attempting comprehensive transformation.
High-Impact Automation Examples
Inventory Management: AI systems that automatically reorder materials based on consumption patterns, lead times, and production schedules typically reduce inventory costs by 15-20% while preventing stockouts.
Energy Optimization: Smart systems that adjust HVAC, lighting, and equipment operation based on production schedules and occupancy patterns often reduce energy costs by 10-25%.
Document Processing: AI that extracts data from invoices, purchase orders, and quality certificates eliminates manual data entry while reducing processing errors by 80-90%.
Measuring Automation Impact
Successful automation projects establish clear metrics before implementation:
- Time savings - Hours saved per day/week
- Error reduction - Percentage decrease in mistakes
- Cost savings - Direct cost reductions
- Throughput improvement - Increased production capacity
- Quality enhancement - Defect rate improvements
Building Automation Capabilities
Organizations build automation capabilities through:
- Identifying repetitive tasks with clear rules and measurable outcomes
- Starting with low-risk applications that don't impact critical processes
- Documenting current processes before automation
- Training staff on new automated systems
- Monitoring results and refining automation rules
Real-World Success Stories and Measurable Outcomes
Manufacturing Efficiency Gains
MANTEC reports that AI-driven manufacturing can boost efficiency by 20-40% and cut costs by 15-25%. These improvements come from optimized processes, reduced waste, and better resource utilization across multiple operational areas.
An automotive parts manufacturer implemented comprehensive AI systems across their production line. The initiative included predictive maintenance, quality control automation, and production scheduling optimization. Results after 18 months:
- 35% reduction in unplanned downtime
- 28% improvement in first-pass quality rates
- 22% increase in overall equipment effectiveness
- $2.3 million annual cost savings
Predictive Maintenance Success
A food processing company deployed AI-powered predictive maintenance across their packaging equipment. The system monitors vibration, temperature, and power consumption to predict bearing failures, motor issues, and mechanical wear.
Measurable outcomes:
- 45% reduction in maintenance costs
- 60% decrease in unplanned downtime
- 30% extension of equipment lifespan
- 18-month ROI on AI investment
Quality Control Transformation
An electronics manufacturer replaced manual inspection with AI-powered vision systems on their surface-mount technology (SMT) lines. The system inspects every component placement and solder joint using high-resolution cameras and machine learning algorithms.
Results achieved:
- 99.7% defect detection accuracy
- 50% faster inspection speeds
- 75% reduction in customer returns
- 40% decrease in rework costs
ROI analysis dashboard showing cost savings and payback period calculations.
Supply Chain Optimization
An industrial equipment manufacturer implemented AI for supply chain optimization, analyzing supplier performance, demand patterns, and logistics costs to optimize procurement and inventory decisions.
Measured improvements:
- 20% reduction in inventory carrying costs
- 15% improvement in supplier on-time delivery
- 25% decrease in expedited shipping costs
- 12% improvement in cash flow from reduced inventory
Energy Management Success
A steel manufacturing facility deployed AI-powered energy management that optimizes power consumption across furnaces, motors, and facility systems based on production schedules and energy pricing.
Documented results:
- 18% reduction in energy costs
- 12% decrease in peak demand charges
- 8% improvement in overall energy efficiency
- $850,000 annual savings
Cost Reduction and ROI Analysis
According to research from M1-Project, AI significantly optimizes business processes, leading to cost reduction through improved efficiency and speed, with companies achieving long-term savings by implementing AI technologies strategically.
Direct Cost Reduction Areas
Labor Cost Optimization: AI automation reduces manual tasks while redeploying human workers to higher-value activities. Typical savings range from 10-30% of labor costs in automated processes.
Material Waste Reduction: AI-powered process control and quality systems reduce material waste by optimizing parameters and catching defects earlier in production. Organizations commonly achieve 5-15% reductions in material costs.
Energy Cost Savings: Intelligent energy management systems optimize power consumption based on production needs, utility rates, and equipment efficiency. Energy cost reductions of 10-25% are typical.
Maintenance Cost Reduction: Predictive maintenance prevents costly emergency repairs while optimizing maintenance schedules. Organizations typically see 20-40% reductions in maintenance costs.
ROI Calculation Framework
Successful AI implementations follow a structured ROI analysis:
Initial Investment Costs:
- Software licensing and implementation
- Hardware and infrastructure
- Training and change management
- System integration and customization
Ongoing Operational Costs:
- Software maintenance and updates
- Data storage and processing
- Staff training and support
- System monitoring and optimization
Quantifiable Benefits:
- Labor cost savings
- Material waste reduction
- Energy cost savings
- Maintenance cost reduction
- Quality improvement value
- Increased throughput revenue
Typical ROI Timeline: Most manufacturing AI implementations achieve positive ROI within 12-24 months, with full benefits realized within 2-3 years.
Cost Reduction Case Studies
Case Study 1: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
A pharmaceutical company implemented AI across quality control, batch optimization, and predictive maintenance:
- Initial investment: $1.2 million
- Annual cost savings: $2.8 million
- ROI achieved: 14 months
- Primary savings: Reduced batch failures (40%), optimized maintenance (35%), improved yield (25%)
Case Study 2: Food Processing
A food processor deployed AI for demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and energy management:
- Initial investment: $650,000
- Annual cost savings: $1.4 million
- ROI achieved: 11 months
- Primary savings: Inventory reduction (45%), energy optimization (30%), waste reduction (25%)
Implementation Roadmap and Best Practices
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Months 1-2)
Operational Assessment: Evaluate current processes to identify AI opportunities with highest potential impact. Focus on processes with:
- High frequency and volume
- Clear success metrics
- Available data sources
- Significant manual effort
- Quality or efficiency challenges
Data Readiness Evaluation: Assess data quality, availability, and accessibility. Successful AI implementations require:
- Clean, consistent data formats
- Sufficient historical data (typically 6-12 months minimum)
- Real-time data access capabilities
- Proper data governance and security
Technology Infrastructure Review: Evaluate existing systems for AI integration capabilities:
- Network connectivity and bandwidth
- Computing and storage capacity
- Integration with current MES/ERP systems
- Security and compliance requirements
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation (Months 3-6)
Select High-Impact Use Case: Choose a pilot project with:
- Clear, measurable success criteria
- Limited scope and risk
- Strong stakeholder support
- Available champion and resources
Develop Minimum Viable Product (MVP): Create a basic AI system that demonstrates core functionality and value. Focus on:
- Core algorithm development and training
- Basic user interface and integration
- Essential monitoring and reporting
- Proof-of-concept validation
Measure and Validate Results: Establish baseline metrics and track improvements:
- Quantitative measurements (time, cost, quality, efficiency)
- Qualitative feedback from users and stakeholders
- Technical performance metrics (accuracy, reliability, speed)
- Business impact assessment
Phase 3: Scaling and Expansion (Months 7-12)
Refine and Optimize: Improve the pilot system based on lessons learned:
- Algorithm refinement and retraining
- User interface improvements
- Integration enhancements
- Performance optimization
Expand to Similar Applications: Apply proven approaches to related use cases:
- Replicate successful patterns
- Leverage existing data and infrastructure
- Build on established user acceptance
- Maintain focus on measurable outcomes
Develop Internal Capabilities: Build organizational AI expertise:
- Train technical staff on AI systems
- Develop data management capabilities
- Establish AI governance processes
- Create change management programs
Phase 4: Integration and Optimization (Months 13-18)
System Integration: Connect multiple AI applications for broader optimization:
- Data sharing between AI systems
- Coordinated decision-making processes
- Unified monitoring and management
- Enterprise-wide optimization
Advanced Analytics: Implement sophisticated AI capabilities:
- Multi-variable optimization
- Predictive analytics and forecasting
- Automated decision-making
- Continuous learning and improvement
Performance Monitoring: Establish ongoing monitoring and optimization:
- Real-time performance dashboards
- Automated alert systems
- Regular model retraining and updates
- Continuous improvement processes
Best Practices for Success
Start Small and Scale Gradually: MIT Sloan Management Review emphasizes the importance of small-scale transformations to minimize risk while achieving measurable outcomes. Begin with focused pilot projects that demonstrate clear value before expanding to broader applications.
Focus on Data Quality: High-quality, well-organized data is essential for AI success. Invest in data cleaning, standardization, and governance before implementing AI systems.
Engage Stakeholders Early: Involve operators, managers, and other stakeholders in the planning and implementation process. Their expertise and buy-in are critical for successful adoption.
Measure Everything: Establish clear metrics and tracking systems to measure AI impact. Regular measurement enables continuous improvement and demonstrates business value.
Plan for Change Management: AI implementation requires changes to processes, roles, and workflows. Invest in training, communication, and support to ensure smooth transitions.
Maintain Realistic Expectations: Set achievable goals and timelines. Overly ambitious expectations can lead to disappointment and reduced support for AI initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can AI improve manufacturing processes?
AI improves manufacturing processes by enhancing predictive maintenance, optimizing scheduling, and improving quality control. These improvements lead to reduced downtime, increased efficiency, and higher product quality.
How long does it typically take to see results from AI implementation in manufacturing?
Most manufacturing AI implementations show initial results within 3-6 months, with significant measurable improvements typically achieved within 6-12 months. Predictive maintenance applications often demonstrate value within 60-90 days, while more complex process optimization projects may require 9-12 months to show full benefits. The timeline depends on data availability, system complexity, and implementation scope.
What's the minimum data requirement for AI systems to work effectively?
AI systems generally require 6-12 months of historical data for initial training, though some applications can work with less. The key factors are data quality, consistency, and relevance rather than pure volume. For predictive maintenance, 3-6 months of sensor data may be sufficient, while demand forecasting typically requires 12-24 months of historical sales data. Clean, well-structured data is more valuable than large volumes of inconsistent information.
How do AI systems integrate with existing manufacturing equipment and software?
Modern AI systems integrate through APIs, standard industrial protocols (OPC-UA, Modbus), and edge computing devices that connect to existing sensors and control systems. Most implementations don't require replacing current equipment but instead add intelligence layers that work with existing MES, ERP, and SCADA systems. Edge computing enables local data processing and decision-making while maintaining connectivity to cloud-based AI services.
What skills do our staff need to manage AI systems?
Staff need basic understanding of AI concepts, data interpretation skills, and training on specific AI system interfaces. Technical staff should understand data quality requirements, system monitoring, and basic troubleshooting. Most AI systems are designed for operation by existing manufacturing personnel with appropriate training rather than requiring specialized AI expertise. Focus training on system operation, result interpretation, and when to seek technical support.
How do we measure the ROI of AI investments in manufacturing?
ROI measurement should include direct cost savings (labor, materials, energy, maintenance), productivity improvements (throughput, quality, efficiency), and risk reduction (downtime prevention, quality issues). Establish baseline metrics before implementation and track improvements monthly. Typical payback periods range from 12-24 months, with annual returns of 150-300% common for successful implementations. Include both hard savings (reduced costs) and soft benefits (improved decision-making, better planning).
What are the biggest risks in manufacturing AI implementation?
Primary risks include poor data quality leading to inaccurate results, over-reliance on AI without human oversight, inadequate change management causing user resistance, and unrealistic expectations about AI capabilities. Technical risks include system integration challenges, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and algorithm bias. Mitigate risks through pilot projects, proper data governance, comprehensive training, and maintaining human oversight of critical decisions.
Can AI work with our legacy manufacturing equipment?
Yes, AI can work with legacy equipment through retrofit sensors, edge computing devices, and integration platforms that connect older systems to modern AI applications. Many successful implementations involve adding sensors and connectivity to existing equipment rather than replacement. The key is identifying what data can be extracted from current systems and how AI can provide value without requiring major equipment investments.
How do we ensure AI recommendations are accurate and reliable?
Ensure accuracy through proper data validation, algorithm testing with historical data, continuous monitoring of AI performance, and maintaining human oversight for critical decisions. Implement confidence scoring that indicates AI certainty levels, establish exception handling for unusual situations, and regularly retrain models with new data. Set up automated alerts for when AI recommendations fall outside normal parameters or confidence thresholds.
What's the difference between AI and traditional automation in manufacturing?
Traditional automation follows pre-programmed rules and sequences, while AI systems learn from data and adapt to changing conditions. AI can handle variability, uncertainty, and complex decision-making that rule-based automation cannot. AI systems improve over time through machine learning, while traditional automation requires manual programming changes. AI excels at pattern recognition, prediction, and optimization, while traditional automation handles repetitive, well-defined tasks.
How do we get started with AI if we have limited technical expertise?
Start with vendor-supported solutions that include implementation services, training, and ongoing support. Focus on proven applications like predictive maintenance or quality control that have established success patterns. Partner with technology providers or consultants who specialize in manufacturing AI implementations. Begin with pilot projects that have clear success criteria and limited scope, then build internal capabilities gradually as you gain experience and demonstrate value.
Conclusion: Making AI Work for Your Operations
AI transforms manufacturing operations not through revolutionary disruption, but through practical improvements to existing processes. The most successful implementations focus on specific operational challenges—predictive maintenance, quality control, scheduling optimization, or energy management—where AI can deliver measurable improvements.
The key to AI success lies in matching technology capabilities to real operational needs rather than pursuing abstract transformation goals. Organizations that achieve the best results start with clear problems, implement focused solutions, and expand systematically based on proven outcomes.
Modern AI systems work alongside existing equipment, processes, and personnel to enhance decision-making and optimize performance. This collaborative approach reduces implementation risk while maximizing the value of current investments in equipment and expertise.
The evidence from successful implementations is compelling: AI-driven manufacturing can boost efficiency by 20-40% and cut costs by 15-25% when applied strategically to high-impact processes. These improvements come from better prediction, faster detection, optimized scheduling, and reduced waste rather than wholesale process replacement.
For operations leaders considering AI implementation, the path forward is clear: identify specific operational challenges where AI can add value, start with focused pilot projects, measure results carefully, and scale successful applications systematically. The technology is proven, the benefits are measurable, and the competitive advantages are real for organizations that move beyond buzzwords to practical implementation.
The question isn't whether AI will transform manufacturing—it's already happening. The question is whether your organization will lead or follow in applying these powerful tools to create sustainable competitive advantages through operational excellence.
Modern manufacturing facility showing integrated AI systems, human operators, and optimized production processes working together.
More Blog Posts

AI Agents: The Next Generation of Business Software Transforming Operations
Discover how AI agents are revolutionizing business operations by transforming software into proactive collaborators that anticipate needs and streamline complex processes autonomously.

AI Agents in Enterprise Workflows: Transforming Business Operations for 2026
Discover how AI agents are revolutionizing enterprise workflows, transforming businesses into proactive, autonomous entities that enhance efficiency and drive measurable value.

Scaling AI Solutions: From Prototype to Production Best Practices
Learn how to successfully scale AI solutions from prototype to production, focusing on key practices that align data engineering with business goals, especially in healthcare.