
AI Readiness Assessment: The Complete Guide to Preparing Your Company for Intelligent Automation
Discover why AI readiness is crucial for success in automation, focusing on data quality, workforce capabilities, and governance to avoid the pitfalls of failed projects.
AI Readiness: Preparing for Intelligent Automation
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, AI readiness is not just an option—it's a necessity for staying competitive. AI readiness extends far beyond having the latest technology—it requires a comprehensive evaluation of your organization's data quality, governance structures, workforce capabilities, and operational alignment. Before deploying AI solutions, companies must assess whether their foundational elements can support intelligent automation effectively.
The stakes are high: 70% of AI projects fail due to inadequate readiness assessments, while organizations that conduct proper evaluations increase their success likelihood by 47%. This stark reality underscores why preparation determines success more than algorithms themselves.
What Is AI Readiness and Why It Matters
What is AI readiness?
AI readiness is the organizational capacity to successfully implement, manage, and derive value from artificial intelligence technologies across technical infrastructure, data foundations, governance frameworks, and human capabilities.
The current landscape reveals both opportunity and challenge. According to a 2024 McKinsey survey, 75% of businesses have adopted AI in at least one function, with 65% using generative AI regularly. However, success rates remain concerning—over half of employees feel untrained for AI roles, and nearly half of employers cite unprepared data as a primary implementation barrier.
AI readiness assessment can increase implementation success rates by 47% when conducted properly. This improvement stems from identifying critical gaps before they become costly failures, similar to how IBM's Watson project struggled due to insufficient preparation and unrealistic expectations.

A balanced scale with AI technology on one side and organizational readiness elements like data quality, governance, workforce, and opera...
The distinction between AI adoption and AI readiness is crucial. Adoption means implementing AI tools; readiness means your organization can sustain, govern, and extract measurable value from these implementations over time.
The Five Pillars of AI Readiness
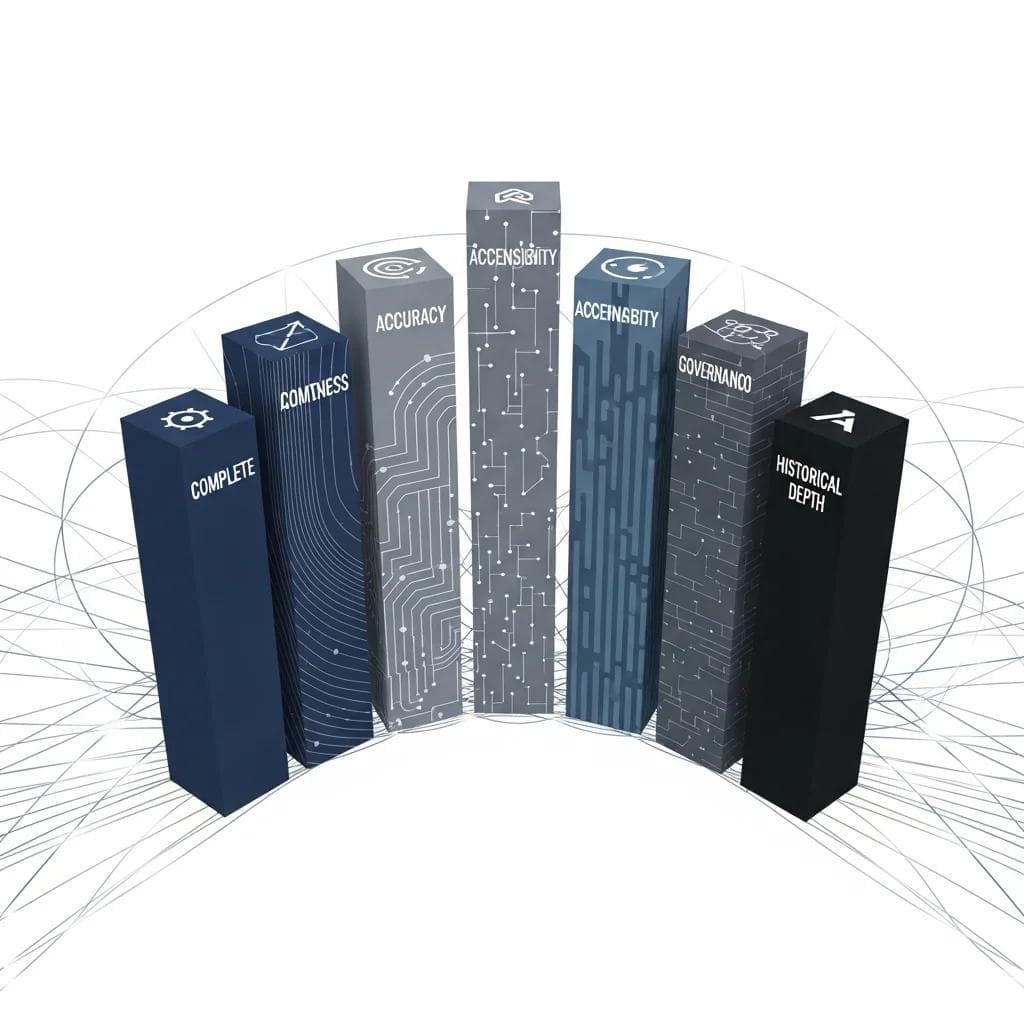
Data Quality and Infrastructure Foundation
Your data serves as the fuel for AI systems, making quality assessment the first critical checkpoint. Organizations with poor data quality face a 23% higher risk of AI project failure, as inadequate data foundations cannot support reliable intelligent automation.
Data readiness evaluation checklist:
- Data completeness: Are critical data points consistently captured across systems?
- Data accuracy: How frequently do data validation errors occur?
- Data accessibility: Can AI systems access required data without significant integration work?
- Data governance: Are there clear ownership, lineage, and quality standards?
- Historical depth: Is there sufficient historical data for training and validation?
Common data quality issues include inconsistent formatting across systems, missing values in critical fields, outdated information, and siloed data repositories that resist integration. Organizations must audit their data landscape before AI implementation, identifying gaps that could undermine system performance.
Infrastructure assessment focuses on computational capacity, storage scalability, and integration capabilities. Modern AI workloads demand significant processing power, especially for machine learning training and real-time inference. Cloud-native architectures often provide the flexibility needed for AI scaling, but on-premises systems require careful capacity planning.

A series of interconnected pillars, each a data quality checkpoint, arranged in a semi-circle, with each pillar having unique textures an...
Governance and Risk Management Framework
AI governance encompasses the policies, procedures, and oversight mechanisms that ensure responsible, compliant, and effective AI deployment throughout an organization.
The urgency of governance has intensified with regulatory developments. The EU's Digital Operational Resilience Act and similar regulations worldwide require organizations to demonstrate responsible AI practices. A Gartner poll indicated that 68% of executives believe generative AI benefits outweigh risks, yet without governance, organizations face potential legal penalties and reputational damage.
Essential governance components include:
Risk assessment protocols that evaluate potential bias, privacy violations, security vulnerabilities, and operational disruptions. Each AI use case requires specific risk evaluation, from customer-facing chatbots that might generate inappropriate responses to predictive maintenance systems that could recommend unsafe procedures.
Compliance frameworks aligned with industry standards like NIST AI Risk Management Framework and ISO/IEC 42001. These frameworks provide structured approaches to AI governance, helping organizations establish consistent practices across different AI initiatives.
Cross-functional governance teams involving legal, compliance, IT, business stakeholders, and ethics specialists. Effective governance requires diverse perspectives to identify risks that technical teams might overlook.
Continuous monitoring systems that track AI performance, detect drift, and flag potential issues before they impact operations. This includes model performance metrics, fairness assessments, and security monitoring.
Skills and Workforce Capabilities
The human element often determines AI success more than technical sophistication. Organizations must evaluate existing capabilities and identify skill gaps across technical implementation, business integration, and strategic management.
Technical skills assessment covers:
- Data science and machine learning expertise for model development and optimization
- Software engineering capabilities for AI system integration and deployment
- Data engineering skills for pipeline creation and maintenance
- DevOps and MLOps knowledge for automated model lifecycle management
Business integration skills include:
- Change management expertise to guide organizational transformation
- Process analysis capabilities to identify optimal AI implementation points
- Project management skills specific to AI initiatives with their unique challenges
- Domain expertise to ensure AI solutions address real business problems effectively
Strategic leadership capabilities encompass:
- AI literacy among executives and decision-makers
- Vision development for AI integration across business functions
- Investment prioritization skills to allocate resources effectively
- Risk assessment abilities to balance innovation with prudent management
Rather than solely hiring external experts, successful organizations focus on reskilling existing employees who understand company culture, processes, and domain-specific requirements. This approach builds sustainable internal capabilities while maintaining institutional knowledge.

A matrix of interconnected blocks, each block a different skill area, vibrant colors for technical, business, and strategic capabilities,...
Integration and Change Management
Successful AI implementation requires seamless integration with existing systems, processes, and organizational culture—areas where technical capability alone proves insufficient.
Integration challenges span multiple dimensions:
Technical integration involves connecting AI systems with existing software, databases, and workflows. Legacy systems often resist modern AI tools, requiring middleware solutions, API development, or system modernization. Organizations must evaluate their technical debt and integration complexity before AI deployment.
Process integration requires redesigning workflows to incorporate AI insights and automation. This might involve changing approval processes, modifying quality control procedures, or restructuring decision-making hierarchies. Resistance to change affects 67% of AI implementations, making change management a critical success factor.
Cultural integration addresses human resistance, fear of job displacement, and skepticism about AI capabilities. Successful organizations invest heavily in communication, training, and demonstrating AI's role as an augmentation tool rather than replacement technology.
Change management strategies include:
- Pilot programs that demonstrate value in low-risk environments
- Champion networks that advocate for AI adoption across departments
- Communication campaigns that address concerns transparently
- Training programs that build confidence in AI tools
- Success metrics that clearly show AI's positive impact
Operational Fit and Strategic Alignment
AI readiness requires alignment between AI capabilities and actual business needs, ensuring that intelligent automation addresses real operational challenges rather than pursuing technology for its own sake.
Strategic alignment assessment examines:
Business case development that clearly articulates expected ROI, implementation costs, and success metrics. Many AI projects fail because they lack clear business justification beyond technological novelty.
Use case prioritization that identifies high-impact, low-risk opportunities for initial AI deployment. Successful organizations often start with operational efficiency improvements before moving to customer-facing applications.
Resource allocation that balances AI investments with other business priorities. AI requires sustained investment in technology, training, and organizational change—commitments that must align with overall business strategy.
Competitive positioning that leverages AI for sustainable advantage rather than temporary efficiency gains. This requires understanding how AI can enhance core value propositions and differentiate market offerings.

Four interconnected puzzle pieces, each a different aspect of strategic alignment: business case, use cases, resources, competitive posit...
The Complete AI Readiness Assessment Framework
Assessment Methodology
A comprehensive AI readiness assessment evaluates organizational preparedness across seven interconnected dimensions, requiring approximately 45 minutes of structured evaluation by cross-functional teams.
Microsoft's AI Readiness Assessment framework provides a proven methodology covering:
- Business Strategy: Leadership vision, investment alignment, and strategic objectives
- AI Governance & Security: Risk management, compliance frameworks, and ethical guidelines
- Data Foundations: Quality, accessibility, and governance of data assets
- AI Strategy & Experience: Previous AI initiatives, lessons learned, and capability development
- Organization & Culture: Change readiness, skill availability, and cultural factors
- Infrastructure for AI: Technical capacity, integration capabilities, and scalability
- Model Management: Lifecycle processes, monitoring systems, and maintenance procedures
Scoring and Interpretation
Assessment results identify organizational strengths and improvement areas through standardized scoring across each dimension. Organizations scoring below 60% in any dimension face significantly higher implementation risks and should address gaps before AI deployment.
Scoring interpretation guidelines:
- 90-100%: Excellent readiness, suitable for advanced AI initiatives
- 75-89%: Good readiness, minor gaps to address
- 60-74%: Moderate readiness, significant preparation needed
- Below 60%: Poor readiness, foundational work required
Common assessment findings reveal that most organizations excel in strategic vision but struggle with data quality and governance frameworks. Technical infrastructure often receives mid-range scores, while workforce capabilities show the widest variation across industries and company sizes.
Action Planning Based on Assessment Results
Assessment results must translate into specific action plans with timelines, resource requirements, and success metrics for each identified gap.
Priority-based improvement roadmaps typically follow this sequence:
Phase 1: Foundation Building (0-6 months)
- Data quality improvement initiatives
- Basic governance framework establishment
- Initial skill gap assessment and training program design
- Quick-win pilot project identification
Phase 2: Capability Development (6-12 months)
- Advanced training program implementation
- Integration architecture development
- Governance process refinement
- Expanded pilot programs
Phase 3: Scale and Optimization (12-24 months)
- Full-scale AI deployment
- Advanced governance and monitoring
- Continuous improvement processes
- Strategic advantage development

A series of interconnected stepping stones leading through a lush garden, each stone a phase in a journey, with varying textures and colo...
Common AI Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Overcoming Data Quality Obstacles
Poor data quality represents the most common AI implementation barrier, affecting nearly half of all organizations attempting intelligent automation deployment.
Data quality challenges manifest in multiple forms:
Inconsistent data formats across systems create integration nightmares. Customer information might exist in different formats across CRM, billing, and support systems, requiring extensive normalization before AI processing.
Missing or incomplete data undermines model training and prediction accuracy. Historical records often lack critical fields, seasonal data might be missing, or recent system changes might have created data gaps.
Data silos prevent comprehensive analysis by isolating information within departmental boundaries. Sales, marketing, and customer service might maintain separate customer databases with overlapping but inconsistent information.
Solutions for data quality improvement:
- Implement data profiling tools to identify quality issues systematically
- Establish data stewardship roles with clear accountability for data quality
- Create automated data validation processes that flag quality issues in real-time
- Develop data integration platforms that normalize formats across systems
- Invest in master data management systems that maintain single sources of truth
Addressing Workforce Resistance and Skills Gaps
Human factors account for 60% of AI implementation failures, making workforce preparation as critical as technical readiness.
Resistance patterns include fear of job displacement, skepticism about AI capabilities, and comfort with existing processes. Successful organizations address these concerns through transparent communication, inclusive planning, and demonstrable value creation.
Skills gap solutions:
- Partner with educational institutions for customized training programs
- Implement mentorship programs pairing AI-experienced staff with domain experts
- Create internal certification programs that validate AI competencies
- Establish communities of practice for knowledge sharing and collaboration
- Invest in hands-on learning platforms that provide practical AI experience
Managing Integration Complexity
Legacy system integration represents a significant challenge for 73% of organizations implementing AI, requiring careful planning and often substantial technical investment.
Integration complexity stems from outdated APIs, incompatible data formats, security restrictions, and performance limitations. Modern AI systems often require real-time data access and high-throughput processing capabilities that legacy systems cannot provide.
Integration strategies:
- Develop API-first architectures that facilitate future AI integration
- Implement middleware solutions that bridge legacy and modern systems
- Create data lakes that consolidate information from multiple sources
- Establish microservices architectures that enable modular AI deployment
- Plan system modernization roadmaps that align with AI requirements
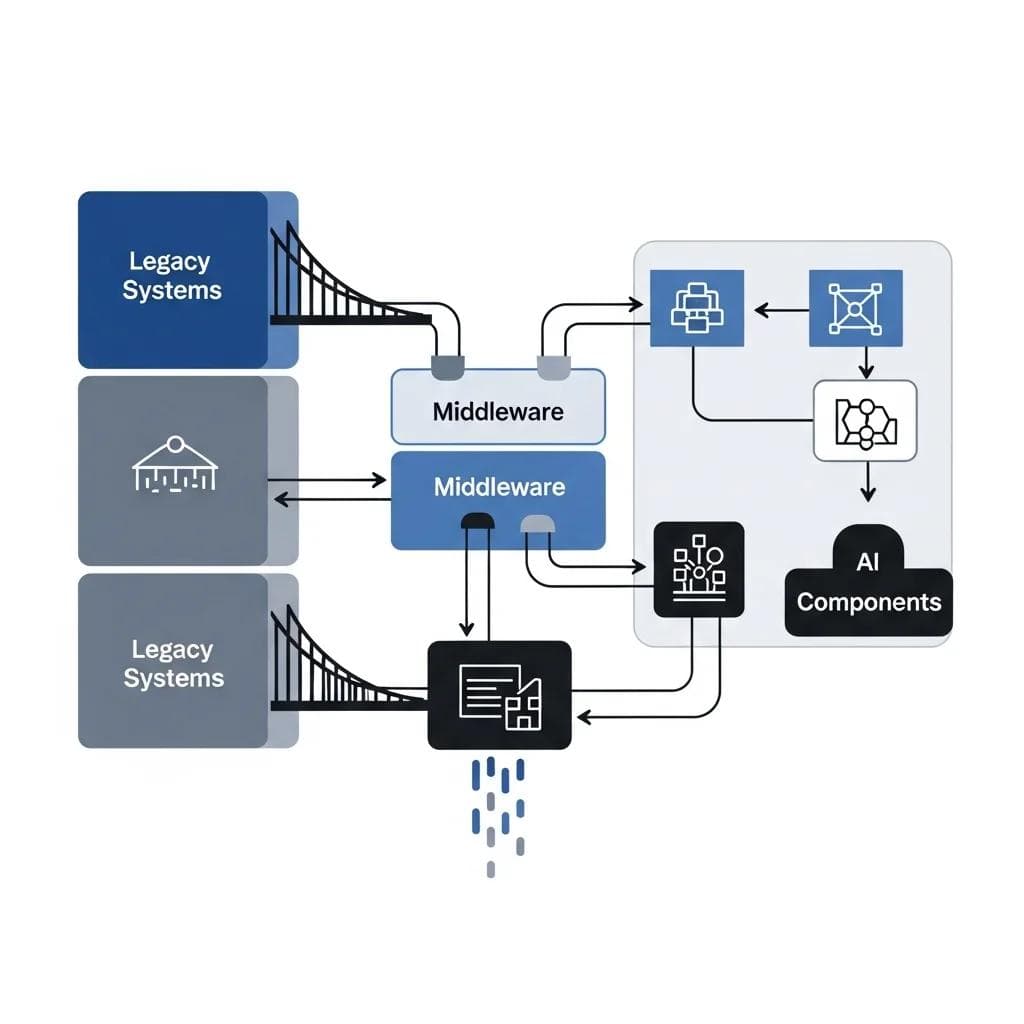
Diagram with interconnected blocks, showing legacy systems on one side, middleware in the center, AI components on the other side, arrows...
Building Your AI Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation Assessment and Planning
The foundation phase establishes baseline readiness and creates detailed implementation plans based on comprehensive organizational assessment.
Foundation activities include:
Stakeholder alignment ensures executive sponsorship, cross-functional support, and clear success criteria. AI initiatives require sustained commitment and resources that only strong leadership support can provide.
Pilot project selection identifies low-risk, high-value opportunities for initial AI deployment. Successful pilots demonstrate capability, build confidence, and provide learning opportunities for larger initiatives.
Resource planning determines budget requirements, staffing needs, and technology investments necessary for successful implementation. This includes both direct AI costs and supporting infrastructure, training, and change management expenses.
Risk assessment identifies potential challenges, mitigation strategies, and contingency plans. Early risk identification prevents costly surprises and enables proactive management.
Phase 2: Capability Building and Pilot Execution
The capability building phase develops necessary skills, establishes governance processes, and executes pilot projects that demonstrate AI value.
Key capability building activities:
Training program implementation provides hands-on AI experience for technical staff, business users, and leadership teams. Effective training combines theoretical knowledge with practical application in organizational context.
Governance framework activation establishes oversight processes, compliance procedures, and performance monitoring systems. This includes creating AI ethics committees, defining approval processes, and implementing risk management protocols.
Technology infrastructure development creates the technical foundation necessary for AI deployment. This might involve cloud platform setup, data pipeline creation, or security framework implementation.
Pilot project execution provides real-world experience with AI implementation while generating measurable business value. Successful pilots create momentum for broader AI adoption.
Phase 3: Scaling and Optimization
The scaling phase expands successful AI implementations across the organization while continuously optimizing performance and value creation.
Scaling considerations include:
Process standardization creates repeatable methodologies for AI project implementation, reducing costs and risks for future initiatives.
Center of excellence establishment centralizes AI expertise, best practices, and support services for organization-wide AI initiatives.
Continuous improvement processes monitor AI performance, identify optimization opportunities, and ensure sustained value creation.
Strategic integration aligns AI capabilities with long-term business strategy, competitive positioning, and market opportunities.
A horizontal timeline with three distinct phases, each phase by a different color, connected by arrows, key milestones depicted as icons...
Measuring AI Readiness Success
Key Performance Indicators
Effective AI readiness measurement requires balanced scorecards that track technical capabilities, business outcomes, and organizational development across multiple timeframes.
Technical readiness metrics:
- Data quality scores across completeness, accuracy, and consistency dimensions
- System integration success rates and performance benchmarks
- Infrastructure utilization and scalability measurements
- Model performance and reliability statistics
Business readiness metrics:
- Employee AI literacy assessment scores
- Change management effectiveness indicators
- Process integration success rates
- Governance compliance measurements
Outcome metrics:
- AI project success rates compared to industry benchmarks
- Time-to-value for AI implementations
- Return on investment from AI initiatives
- Business process improvement measurements
Continuous Assessment and Improvement
AI readiness is not a one-time achievement but an ongoing capability that requires continuous evaluation and enhancement as technology and business requirements evolve.
Regular reassessment schedules should occur quarterly for rapidly changing areas like technology infrastructure and skills development, while strategic alignment and governance frameworks might require annual comprehensive reviews.
Continuous improvement processes include:
- Regular skills gap analysis as AI technology advances
- Data quality monitoring with automated alerting for degradation
- Governance framework updates reflecting regulatory changes
- Technology infrastructure capacity planning and optimization
- Competitive analysis to ensure AI capabilities remain relevant
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the minimum time required for AI readiness assessment?
A basic AI readiness assessment takes approximately 45 minutes using structured frameworks like Microsoft's evaluation tool. However, comprehensive organizational assessment including detailed data audits, skills evaluation, and strategic alignment analysis typically requires 2-4 weeks with cross-functional team involvement.
How to prepare for intelligent automation?
Preparing for intelligent automation involves conducting a thorough AI readiness assessment, ensuring data quality, establishing governance frameworks, developing workforce skills, and aligning AI initiatives with strategic business goals.
Challenges in AI implementation for tech companies
Tech companies often face challenges such as data quality issues, integration complexity with legacy systems, workforce resistance, and maintaining governance and compliance in rapidly evolving AI landscapes.
How much should organizations budget for AI readiness preparation?
AI readiness preparation typically costs 15-25% of the total AI implementation budget. For a $1 million AI project, organizations should allocate $150,000-$250,000 for readiness activities including data preparation, training, governance establishment, and change management. This upfront investment significantly improves success rates.
Which AI readiness pillar is most critical for success?
Data quality represents the most critical readiness factor, as poor data undermines all other AI capabilities. However, successful implementations require balanced attention to all five pillars—data, governance, skills, integration, and strategic alignment—as weaknesses in any area can cause project failure.
Can small companies conduct meaningful AI readiness assessments?
Small companies can absolutely conduct effective AI readiness assessments using simplified frameworks focused on their specific use cases. Many assessment tools scale to organizational size, and smaller companies often have advantages in agility and decision-making speed that can accelerate readiness development.
How often should AI readiness be reassessed?
Organizations should conduct comprehensive AI readiness reassessments annually, with quarterly reviews of rapidly changing areas like skills development and technology infrastructure. Major business changes, new AI initiatives, or regulatory updates may trigger additional assessments.
What are the biggest mistakes in AI readiness preparation?
The most common mistakes include focusing exclusively on technology while ignoring human factors, underestimating data preparation requirements, lacking executive sponsorship for sustained commitment, and attempting to implement AI without clear business justification or success metrics.
How long does it take to improve AI readiness scores?
Basic readiness improvements in areas like governance frameworks and initial training can show results within 3-6 months. Comprehensive readiness development including data quality improvement, skills development, and cultural change typically requires 12-18 months for substantial progress.
Should organizations hire external consultants for AI readiness assessment?
External consultants bring valuable objectivity, industry benchmarking, and specialized expertise for AI readiness assessment. However, internal teams must be deeply involved to ensure accurate evaluation and successful implementation of recommendations. The best approach combines external expertise with internal knowledge and commitment.
What role does leadership play in AI readiness?
Leadership commitment is absolutely critical for AI readiness success. Executives must provide sustained sponsorship, resource allocation, and strategic direction while championing cultural change and addressing resistance. Without strong leadership support, AI readiness initiatives typically fail regardless of technical capabilities.
How does AI readiness differ across industries?
AI readiness requirements vary significantly by industry based on regulatory requirements, data sensitivity, operational complexity, and competitive dynamics. Healthcare and financial services face stricter governance requirements, while manufacturing emphasizes integration with existing systems. However, the fundamental readiness pillars remain consistent across industries.
---
AI readiness assessment is not optional—it's the foundation that determines whether your AI investments generate transformative value or join the 70% of failed implementations. Organizations that invest in comprehensive readiness evaluation and preparation position themselves for sustained AI success, competitive advantage, and measurable business transformation.
The path forward requires honest assessment, strategic planning, and sustained commitment to building organizational capabilities that extend far beyond technology adoption. Start with the readiness checklist, identify your gaps, and build the foundation that turns AI ambition into business reality.
More Blog Posts

AI Agents: The Next Generation of Business Software Transforming Operations
Discover how AI agents are revolutionizing business operations by transforming software into proactive collaborators that anticipate needs and streamline complex processes autonomously.

AI Agents in Enterprise Workflows: Transforming Business Operations for 2026
Discover how AI agents are revolutionizing enterprise workflows, transforming businesses into proactive, autonomous entities that enhance efficiency and drive measurable value.

Scaling AI Solutions: From Prototype to Production Best Practices
Learn how to successfully scale AI solutions from prototype to production, focusing on key practices that align data engineering with business goals, especially in healthcare.